Geonet, a vital component in geosynthetics, is revolutionizing industries ranging from civil engineering to environmental management. Its unique properties and versatile applications have made it an indispensable material for professionals seeking efficient, durable, and sustainable solutions. This article delves into the world of geonet, shedding light on its applications, benefits, and frequently asked questions.
What is Geonet?
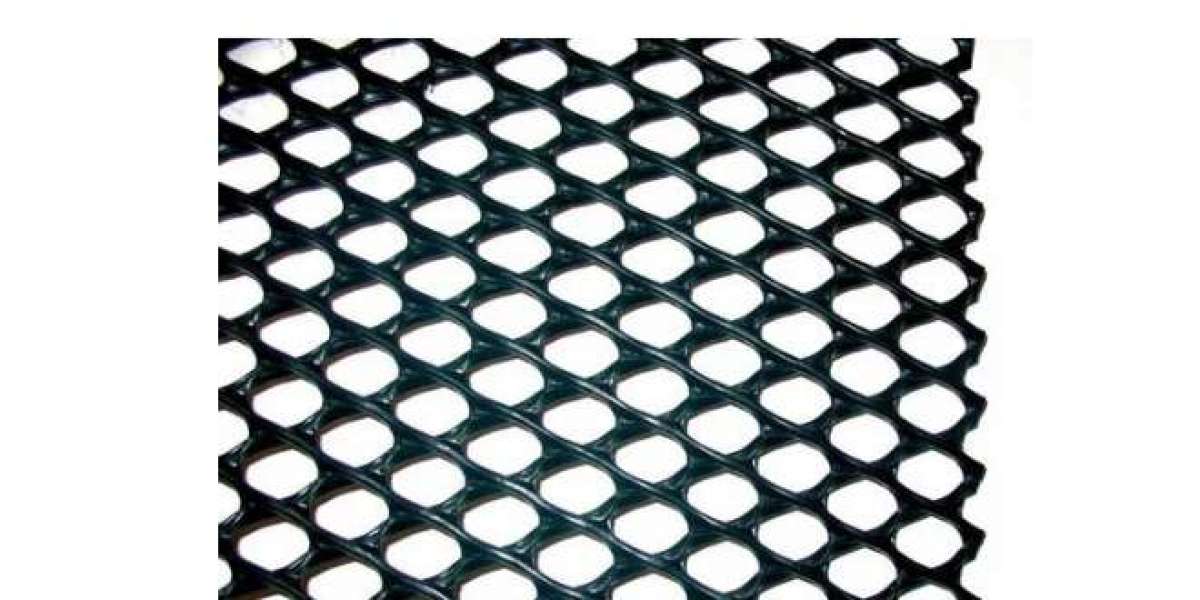
Geonet is a synthetic material designed as a grid-like structure composed of intersecting polymeric ribs. It is primarily used for drainage Pulkit Plastic Products applications in geotechnical engineering, providing high flow capacity and strength. Geonets are manufactured using high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other durable polymers, ensuring longevity and resistance to environmental stressors.
Applications of Geonet
The versatility of Geonet for road stabilization makes it ideal for a wide range of applications. Below are some of the most common uses:
1. Landfill Drainage
Geonets play a critical role in landfill management. Positioned between waste layers and liner systems, they facilitate leachate collection and drainage, preventing environmental contamination.
2. Road and Railway Construction
In road and railway projects, geonets are employed to enhance subgrade drainage. They minimize water accumulation, reducing the risk of pavement failure and improving the longevity of the infrastructure.
3. Erosion Control
Geonets are used to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion. Their grid structure allows vegetation growth while providing structural reinforcement to the soil.
4. Retaining Walls
In retaining wall systems, geonets act as drainage layers, reducing hydrostatic pressure and ensuring structural integrity.
5. Roof Garden Drainage
Geonets provide an efficient drainage solution for rooftop gardens, enabling proper water flow and preventing waterlogging.
6. Mining Applications
In the mining industry, geonets are used for heap leach drainage systems, ensuring effective collection and removal of solutions used in ore processing.
Key Benefits of Geonet
1. High Drainage Efficiency
Geonets are engineered for optimal fluid flow, making them highly effective in applications requiring drainage or leachate management.
2. Durability and Longevity
Manufactured from HDPE or similar materials, Geonet drainage in road construction resist chemical degradation, UV exposure, and physical stress, ensuring long-term performance.
3. Lightweight and Flexible
Despite their strength, geonets are lightweight and easy to install, reducing labor and transportation costs.
4. Environmentally Friendly
By improving water management and reducing erosion, geonets contribute to sustainable construction and environmental preservation.
How Geonet is Made
The manufacturing process of geonet involves extrusion and bonding of polymer strands into a grid-like structure. The process includes:
Material Selection: High-quality polymers, primarily HDPE, are chosen for their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Extrusion: The polymer is melted and extruded into strands.
Bonding: These strands are bonded at intersections to create a uniform grid structure.
Quality Control: The geonet undergoes rigorous testing to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion
Geonets are a cornerstone of modern geotechnical engineering, offering reliable and sustainable solutions for drainage, erosion control, and infrastructure reinforcement. Their durability, efficiency, and versatility make them indispensable in a wide array of applications. Whether in landfill management, road construction, or rooftop gardens, Geonet installation in roadways deliver unmatched performance and long-term benefits.
By understanding the properties and applications of geonets, professionals can make informed decisions to optimize their projects. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, geonets will undoubtedly play an ever-growing role in shaping a resilient and eco-friendly future.
FAQs
1. What are the types of geonet?
Geonets are categorized based on their structure and function:
Biplanar Geonets: Composed of two intersecting layers of strands, providing high drainage capacity.
Triplanar Geonets: Designed with three layers for enhanced strength and flow efficiency.
Composite Geonets: Combine geonet with geotextiles for filtration and drainage functions.
2. How is geonet installed?
The installation process typically involves the following steps:
Preparing the substrate.
Unrolling the geonet over the designated area.
Securing the edges and overlaps.
Placing protective layers, such as geotextiles, if required. Proper installation is crucial to ensure optimal performance.
3. Can geonets be recycled?
Yes, geonets made from HDPE are recyclable. This makes them an eco-friendly choice for projects focused on sustainability.
4. What factors should be considered when choosing a geonet?
Key factors include:
Load-bearing requirements.
Drainage capacity.
Environmental conditions, such as UV exposure and chemical resistance.
Project-specific needs and design requirements.